【webpack】:基础及高级配置
# Webpack 基本配置
下面例子涉及的内容:
拆分配置及 merge
启动本地服务
处理 ES6
处理样式
处理图片
例子:
webpack.common.js 公共配置
module.exports = { entry: `./src/index.js` // 入口文件 module: { rules: [ { // 编译 ES6 test: /\.js$/, // 验证规则 loader: ['babel-loader'], include: './src' // 需要编译的路径 exclude: /node_modules/ // 不需要编译的路径 }, { // 编译 css test: /\.css$/, // loader 的执行顺序是: 从后往前 loader: ['style-loader', 'css-loader'] }, { // css兼容处理 test: /\.css$/, loader: ['style-loader', 'css-loader', 'postcss-loader'] }, { // 编译 less (scss 同理) test: /\.less$/, loader: ['style-loader', 'css-loader', 'less-loader'] } ] }, plugins:[ new HtmlWebpackPlugin({ template: './src/index.html', filename: 'index.html' }) ] }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
341、编译 ES6 是使用 babel,可以在项目的根目录下创建
.babelrc文件,配置编译规则{ "presets": ["@babel/preset-env"], "plugins": [] }1
2
3
4@babel/preset-env:包含了常用的 ES6,ES7,ES8 常用的语法2、
postcss-loader:配置浏览器 css 兼容性。使用时需要在项目根路径下创建postcss.config.jsmodule.exports = { // 增加从 postcss-loader 插件集合中引入添加css前缀插件 plugins: [require("autoprefixer")], };1
2
3
4需要安装
autoprefixer、postcss-loader
webpack.dev.js 开发配置
const webpackCommonConf = require('./webpack.common.js'); const { smart } = require('webpack-merge'); const webpack = require('webpack'); module.exports = smart(webpackCommonConf, { mode: 'development', module: { rules: [ { // 开发环境下图片处理:直接引入 图片 url test: /\.(png|jpg|jpeg|gif)$/, use: 'file-loader' } ] }, plugins: [ new Webpack.DefinePlugin({ // 配置 window.ENV = 'development' ENV: JSON.stringify('development') }) ], devServer: { port: 8080, progress: true, // 显示打包的进度 contentBase: './dist', // 项目根路径 open: true, // 自动打开浏览器 compress: true // 自动 gzip 压缩 } proxy: { // 将本地 /api/xxx 代理到 localhost:3000/api/xxx '/api': 'http://localhost:3000', // 将本地 /api2/xxx 代理到 localhost:3000/xxx '/api2': { target: 'http://localhost:3000', pathRewrite: { '/api2': '' } } } });1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
391、开发环境下启动命令(需要下载 webpack-dev-server)
"dev": "webpack-dev-server --config build-base-conf/webpack.dev.js",12、处理图片:开发环境下使用 url,如果在线上环境下使用 url,对性能方面是比较不友好的
webpack.prod.js 生产配置(线上)
const webpackCommonConf = require('./webpack.common.js'); const { smart } = require('webpack-merge'); module.exports = smart(webpackCommonConf, { mode: 'production', output: { filename: 'bundle.[contentHash:8].js', // 打包代码时,加上 hash 戳 path: './dist' } module: { rules: [ { // 生产环境下图片处理:将比较小的图片地址设置为base64 test: /\.(png|jpg|jpeg|gif)$/, use: { loader: 'url-loader', options: { // 小于 5kb 的图片用 base64 格式产出 // 否则,依然延用 file-loader 的形式,产出 url 格式 limit: 5 * 1024, outputPath: '/img1', // 图片打包到 img1 目录下 } } } ] }, plugins: [ { new ClearWebpackPlugin(), // 会默认清除 output.path 文件夹 new Webpack.DefinePlugin({ // window.ENV = 'production' ENV: JSON.stringify('production') }) } ] })1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
351、生产环境下启动命令
"build": "webpack --config build-base-conf/webpack.prod.js"12、生产环境下将小图片转成 base64 的好处
- 减少 http 请求
- 性能优化
3、打包代码时,加上 hash 戳的好处
- 什么是 hash 戳:根据内容去生产对应的 8 位字符串。只要内容变了,生产的字符串也会进行变化。
- 当内容没有变化时,访问页面,请求 js 文件时,会命中缓存,提高访问速度
测试代码:code/1
# Webpack 高级配置
# 多入口文件
webpack.common.js
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require("html-webpack-plugin"); module.exports = { entry: { // 入口文件 index: "./src/index.js", other: "./src/other.js", }, module: { rules: [], }, plugins: [ // 多入口 - 生成 index.html new HtmlWebpackPlugin({ template: "./src/index.html", filename: "index.html", // chunks 表示该页面要引用哪些 chunk (即上面的 index 和 other),默认全部引用 chunks: ["index"], // 只引用 index.js }), // 多入口 - 生成 other.html new HtmlWebpackPlugin({ template: "./src/other.html", filename: "other.html", chunks: ["other"], // 只引用 other.js }), ], };1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26- webpack.prod.js
const webpackCommonConf = require("./webpack.common.js"); const { smart } = require("webpack-merge"); module.exports = smart(webpackCommonConf, { mode: "production", output: { // 输出: name 对应 entry index 及 other filename: "[name].[contentHash:8].js", path: "./dist", }, });1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# 抽离 CSS 文件
背景:按照 webpack 的基本配置案例中,执行命令npm run dev
在入口文件引入 css 文件:

打包生成后:包含 css
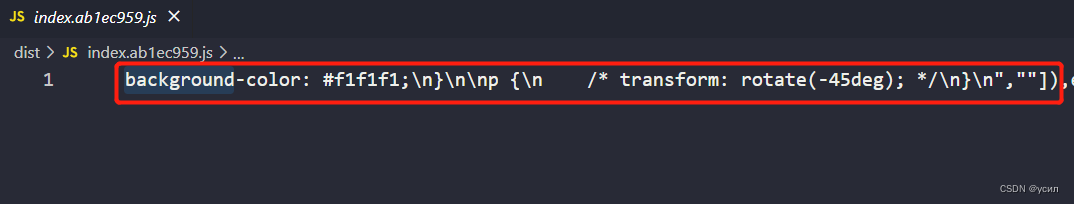 最终在页面中:css 会显示在
最终在页面中:css 会显示在style标签中
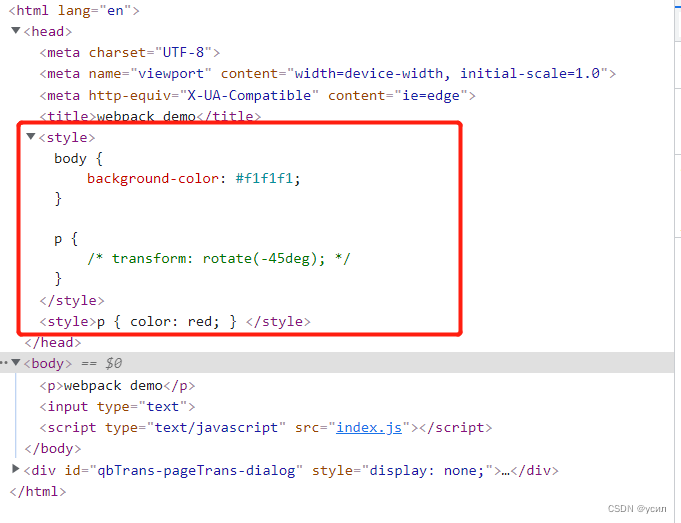
同理执行命令npm run build 也会出现上述情况
测试代码:code/1
对于开发环境下,问题不是很大。
但在线上环境下这种方式是不友好的,正确的做法是:将 css 抽离出来进行打包压缩体积,再已外链的形式引入
由于是针对线上环境:故在webpack.prod.js进行配置
webpack.prod.js
const webpack = require("webpack"); const { smart } = require("webpack-merge"); const { CleanWebpackPlugin } = require("clean-webpack-plugin"); const MiniCssExtractPlugin = require("mini-css-extract-plugin"); const TerserJSPlugin = require("terser-webpack-plugin"); const OptimizeCSSAssetsPlugin = require("optimize-css-assets-webpack-plugin"); const webpackCommonConf = require("./webpack.common.js"); module.exports = smart(webpackCommonConf, { mode: "production", output: { filename: "bundle.[contentHash:8].js", // 打包代码时,加上 hash 戳 path: "./dist", }, module: { rules: [ // 抽离 css { test: /\.css$/, loader: [ MiniCssExtractPlugin.loader, // 注意,这里不再用 style-loader "css-loader", "postcss-loader", ], }, // 抽离 less --> css { test: /\.less$/, loader: [ MiniCssExtractPlugin.loader, // 注意,这里不再用 style-loader "css-loader", "less-loader", "postcss-loader", ], }, ], }, plugins: [ // 抽离 css 文件 new MiniCssExtractPlugin({ filename: "css/main.[contentHash:8].css", }), ], optimization: { // 压缩 css minimizer: [new TerserJSPlugin({}), new OptimizeCSSAssetsPlugin({})], }, });1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49npm run build
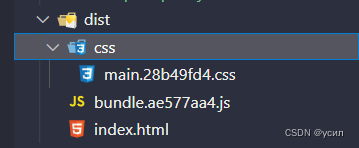
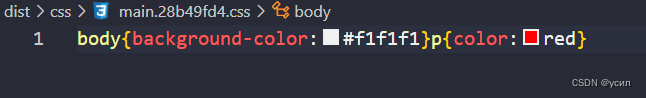
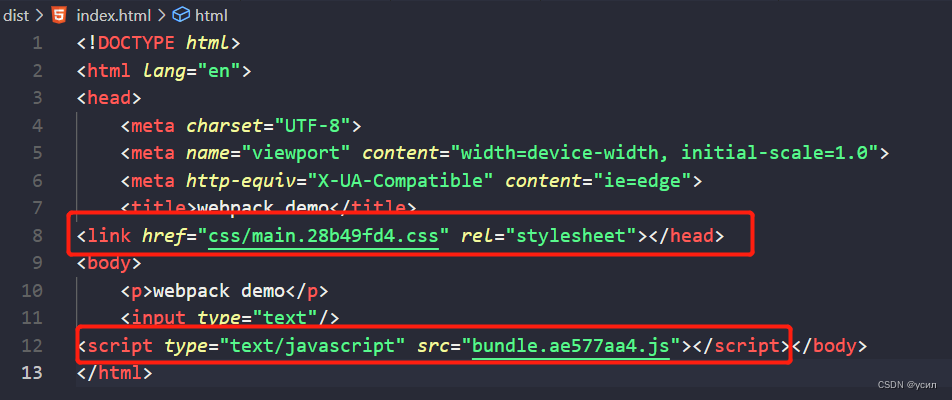
测试代码:code/2
# 抽离公共代码
背景:在多个文件中我们可能会引用同一份代码。比如下面的例子
在入口文件 index.js中引入了math.js文件
import { sum } from "./math";
const sumRes = sum(10, 20);
console.log("sumRes", sumRes);
console.log("index.js");
2
3
4
5
同样在 other.js中也引入 main.js文件
import { sum } from "./math";
const sumRes = sum(10, 20);
console.log("sumRes", sumRes);
console.log("other.js");
2
3
4
5
这样正常打包完成后,就会出现在index.js以及other.js都同时包含了 math 中的代码。
// index.js
const sum = (a, b) => a + b;
const sumRes = sum(10, 20);
console.log("sumRes", sumRes);
console.log("index.js");
// other.js
const sum = (a, b) => a + b;
const sumRes = sum(10, 20);
console.log("sumRes", sumRes);
console.log("other.js");
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
在实际开发环境下问题不是很大,但在线上环境下,如果main.js文件很大的情况下,就会造成文件过大。
正确的做法是:在生产环境下打包,我们应该把公共代码抽离成一个文件,使用是直接使用外链引入即可。
下面以打包两个入口文件为例:
- webpack.common.js
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require("html-webpack-plugin");
module.exports = {
entry: {
index: "./src/index.js",
other: "./src/other.js",
},
module: {},
plugins: [
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
template: "./src/index.html",
filename: "index.html",
// index: 对应 entry 字段 index
// vendor,common: 对应分割代码中的 chunk 分组
chunks: ["index", "vendor", "common"],
}),
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
template: "./src/index.html",
filename: "other.html",
chunks: ["other", "vendor", "common"],
}),
],
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
- webpack.drod.js
const webpackCommonConf = require('./webpack.common.js')
const { smart } = require('webpack-merge')
module.exports = smart(webpackCommonConf, {
mode: 'production',
output: {
filename: '[name].[contentHash:8].js',
path: './dist'
},
module: {},
plugins: [
splitChunks: {
chunks: 'all',
cacheGroups: {
// 第三方包
vendor: {
// chunk 名称
name: 'vendor',
// 优先级 (权限越高,优先抽离)
priority: 1,
test: /node_modules/,
minSize: 0, // 当包大小超过该值100kb时,就抽离出来
minChunks: 1, // 当包被引用次数超过1次,就抽离出来
},
common: {
name: 'common',
priority: 0,
minSize: 0,
minChunks: 2
}
}
}
]
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
上述例子是基于 webpack4.0 版本的,在 webpack5.0 中, 无需配置
chunks: ['other', 'vendor', 'common'],会根据入口文件中引入什么模块就自动引入,就算配置了chunks: ['other', 'vendor', 'common'],也不会生效。
# 懒加载
// index.js
setTimeout(() => {
// 会单独产生一个 chunks
import("./dynamic-data.js").then((res) => {
console.log(res.defult.message);
});
}, 1500);
2
3
4
5
6
7
export default {
message: "this is dynamic data",
};
2
3
webpack 默认支持的语法
# 加载 vue、react
加载 react
// npm install --save-dev @babel/preset-react // .babelrc { "presets": ["@babel/preset-react"], "plugins": [] }1
2
3
4
5
6
7加载 vue
// 下载 vue-loader module.exports = { module: { rules: [ { test: /\.vue$/, loader: ["vue-loader"], include: "./src", }, ], }, };1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12